AI Agents for DIFC Investment Firms: How Gen AI Is Reshaping UAE Wealth Management
A comprehensive guide to understanding AI automation in DIFC-licensed investment advisory and wealth management operations
Your compliance officer just flagged another DFSA deadline. Your relationship managers are buried in quarterly reporting. Your operations team is manually reconciling custodian fees for the third time this week. And your best advisor just told you she spent six hours yesterday on administrative work instead of client meetings.
This isn't a staffing problem—it's a structural problem. And across DIFC, investment firms are discovering that the solution isn't hiring more people. It's fundamentally rethinking how work gets done.
Over the past 18 months, a quiet transformation has begun in Dubai's financial district. Mid-sized investment firms are achieving 40–50% reductions in back-office workload, cutting compliance exceptions by 70%, and recovering hundreds of hours monthly—not through harder work, but through AI agents purpose-built for financial operations.
This guide explains what's actually happening, how the technology works, and what it means for DIFC firms navigating rising regulatory complexity and client expectations that manual processes simply can't meet.
Table of Contents
1. Why DIFC Firms Are Hitting an Operational Ceiling
2. What AI Agents Actually Do (Without the Hype)
3. The Six Core Agents Transforming DIFC Operations
4. How Human-in-the-Loop Governance Works
5. Real Numbers: A DIFC Firm's 90-Day Transformation
6. The Compliance Question: DFSA Requirements and Data Sovereignty
7. Common Questions From DIFC Managing Partners
8. What This Means for Your Firm
Why DIFC Firms Are Hitting an Operational Ceiling
Three converging forces are squeezing DIFC investment firms simultaneously—and traditional solutions aren't working.
Force 1: Regulatory Workload Has Increased 40% Since 2021
DFSA's AML, GEN, and COB modules now require granular transaction tracing that didn't exist four years ago. ESR filings demand detailed documentation of economic substance. FATCA and CRS compliance require cross-border tax verification that changes annually.
The result: what used to be quarterly compliance work now requires continuous monitoring. Firms that managed regulatory obligations with one compliance analyst now need two or three—each costing AED 250K–350K annually.
Force 2: Back-Office Talent Is Expensive and Scarce
DIFC's talent market is competitive. Operations staff with financial services experience command premium salaries. Training new hires takes months. Turnover disrupts continuity.
The math doesn't work: as regulatory obligations grow, firms hire more back-office staff, leaving less budget for revenue-generating roles like business development and client relationship management. Growth stalls because operational costs consume margin.
Force 3: Client Service Expectations Have Fundamentally Shifted
83% of high-net-worth clients now expect real-time portfolio access. Quarterly PDF reports feel archaic. Clients want instant responses to questions about positions, performance, and market events.
Manual workflows can't deliver this. Excel-based reporting takes days or weeks. Email updates require staff time that doesn't scale. Firms lose competitive advantage to more digitally responsive competitors.
The Hidden Cost: 450 Hours Monthly Lost to Administrative Work
A typical 10-person DIFC investment firm loses 450–500 hours every month to non-revenue work:
- KYC and onboarding: 120+ hours collecting documents, verifying identities, checking FATCA/CRS classifications
- Investor reporting: 200+ hours per quarter extracting custodian data, reconciling positions, formatting reports
- Compliance filings: 80+ hours preparing DFSA submissions, maintaining AML registers, tracking deadlines
- Client communication: 60+ hours drafting updates, summarizing meetings, logging CRM activities
That's 2.5 full-time employees working exclusively on operational overhead. For most firms, that represents AED 900K–1.2M in annual labor costs that generate zero revenue and don't scale with AUM growth.
The operational ceiling: advisors can't take on more clients because they're drowning in administrative work for existing ones.
What AI Agents Actually Do (Without the Hype)
Strip away the marketing language, and AI agents are specialized software applications that handle specific, repetitive business workflows autonomously.
Think of them as exceptionally capable junior analysts who never sleep, never make transcription errors, and cost a fraction of human labor. They don't replace professional judgment—they eliminate the grunt work that buries professionals.
How They're Different From Traditional Automation
Traditional robotic process automation (RPA) follows rigid, pre-programmed rules. If a form changes or data appears in an unexpected format, the automation breaks.
AI agents adapt. They interpret unstructured data—scanned passports, email threads, PDF bank statements—and extract relevant information regardless of format variations. They understand context the way humans do, but process it at machine speed.
Example: A traditional RPA bot extracts a client name from a KYC form—but only if the name appears in the exact expected location. An AI agent extracts the name from any document type (passport, utility bill, bank statement) because it understands what "client name" conceptually means.
The Critical Difference: Human-in-the-Loop Architecture
Here's what matters for investment firms: properly designed AI agents don't make final decisions. They draft, suggest, and flag—but humans review and approve.
The AI extracts KYC data from a scanned Emirates ID. A human verifies it's correct before the client record is created. The AI drafts a compliance filing. A compliance officer reviews and approves before submission. The AI generates a portfolio report. An advisor confirms accuracy before client delivery.
This architecture preserves professional accountability while eliminating manual drudgery. The compliance officer's name is on the filing, not the AI's. The advisor owns the client relationship, not the software.
For regulatory purposes, this matters enormously. DFSA inspectors don't audit AI decisions—they audit human decisions supported by AI tools. The audit trail shows what the AI suggested and what the human approved.
The Six Core Agents Transforming investment Operations
Different workflows require different capabilities. Here's what each agent actually does and the problems it solves.
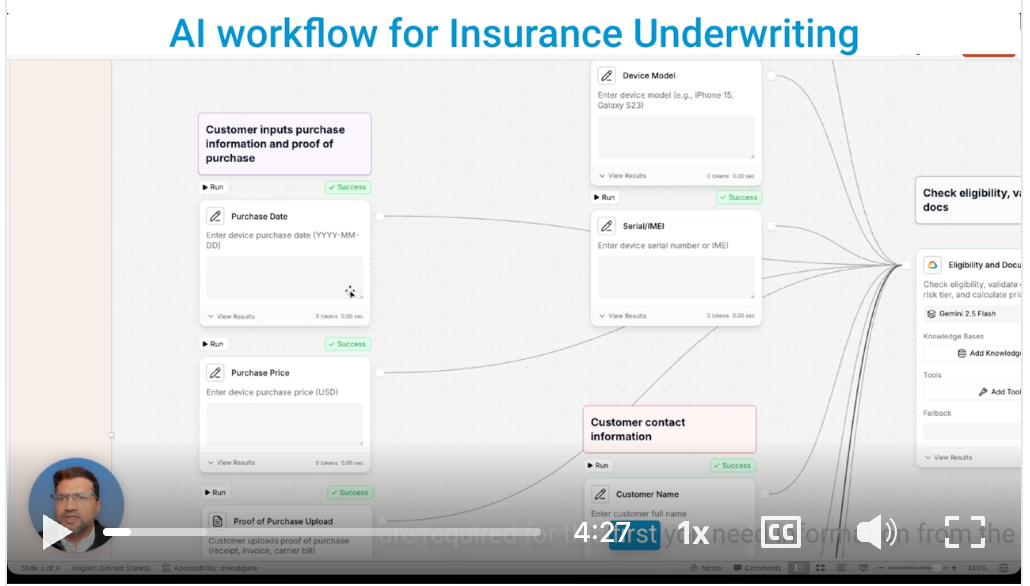
1. KYC & Onboarding Agent
What it does: Extracts information from scanned documents (passports, Emirates IDs, utility bills), validates FATCA classifications against IRS guidelines, verifies CRS tax residency, and populates CRM fields automatically.
The manual alternative: Staff manually type client information from documents into multiple systems, cross-reference tax classifications in PDF rulebooks, and verify addresses against utility bills—9–10 days from inquiry to account activation.
Outcome: Onboarding compressed to 3 days. Firms report 30–50% faster time-to-revenue for new client relationships.
2. Compliance Filing Agent
What it does: Monitors regulatory deadlines, pre-populates DFSA filing templates with data from internal systems, maintains AML registers with automatic transaction flagging, and sends proactive alerts when submissions approach due dates.
The manual alternative: Compliance analysts manually gather transaction data from multiple systems, populate regulatory templates field-by-field, cross-reference internal records, and calendar deadline reminders.
Outcome: Approximately 70% fewer compliance exceptions. Near-elimination of late filing penalties.
3. Fee & Reconciliation Agent
What it does: Matches advisory fee invoices against services rendered, reconciles custodian fee statements against internal billing records, and flags discrepancies for immediate review.
The manual alternative: Operations staff manually compare line items across Excel spreadsheets, investigate breaks, and resolve billing disputes that arise from reconciliation errors.
Outcome: Near-zero reconciliation breaks and dramatic reduction in client billing disputes.
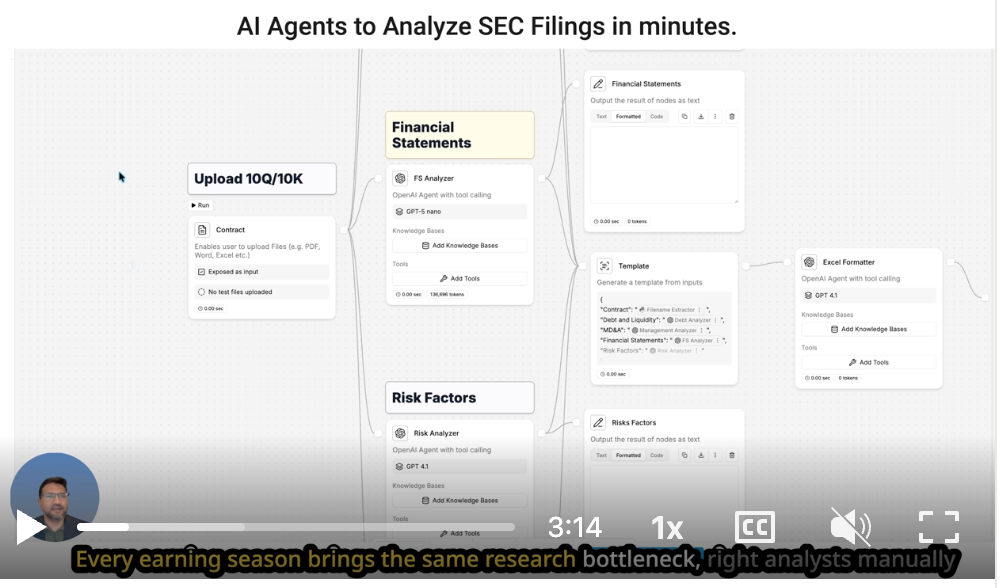
4. Portfolio Report Generator
What it does: Pulls position data from multiple custodian platforms, calculates performance attribution and risk metrics, generates branded PDF reports, and creates interactive Power BI dashboards with real-time data.
The manual alternative: Staff manually extract data from custodian websites, consolidate positions in Excel, calculate returns manually, format reports in Word or PowerPoint—10+ days per quarterly cycle.
Outcome: Reporting cycles shrink from 10 days to 3 days. Clients gain 24/7 dashboard access to current positions.
5. Investor Communication Agent
What it does: Summarizes lengthy email threads into concise bullet points, drafts proactive client update messages based on portfolio events, and suggests personalized insights based on client history.
The manual alternative: Relationship managers read through multi-threaded email conversations, manually draft updates for each client, and struggle to maintain communication consistency across growing client bases.
Outcome: Advisors report 15–20% increase in AUM productivity through time savings. Client satisfaction scores improve measurably.
6. Meeting Summary Agent
What it does: Extracts key decisions and action items from Teams/Zoom meeting transcripts, automatically syncs tasks to CRM with assigned owners and due dates, and distributes follow-up summaries to participants within minutes.
The manual alternative: Someone manually takes meeting notes, types up summaries after the call, and manually creates CRM tasks—hoping nothing important gets missed.
Outcome: Elimination of "dropped ball" scenarios where commitments fall through cracks. Improved client trust and satisfaction.
How Human-in-the-Loop Governance Actually Works
The biggest concern most investment firms have about AI isn't capability—it's accountability. Who's responsible when something goes wrong?
The answer is straightforward: the same people who are responsible now. AI agents don't change accountability—they change what professionals spend time doing.
The Four-Layer Control Framework
Layer 1: AI Executes Defined Tasks
AI agents handle data extraction, document drafting, formatting, pattern recognition, and preliminary analysis. They work at machine speed within carefully defined boundaries.
Layer 2: Human Verifies and Approves
Every client-facing communication and every compliance submission requires explicit human approval. AI drafts; humans review, edit if necessary, and approve. Professional judgment remains exactly where it's always been.
Layer 3: All Actions Logged
Every AI action is timestamped and stored in immutable audit trails. DFSA inspectors can review exactly what the AI did, when it did it, and who approved it. This documentation is actually superior to manual processes, where actions often go unrecorded.
Layer 4: Quarterly Accuracy Audits
Regular reviews ensure AI performance remains within acceptable parameters. Error rates are tracked, and models are refined when performance drifts.
Error Rates: AI-Assisted vs. Fully Manual
Independent testing shows that properly supervised AI agents achieve error rates of 0.1–0.3% on structured tasks like data extraction and compliance checks.
Fully manual human processes typically produce error rates of 2–5% due to fatigue, distraction, and time pressure—particularly during quarter-end reporting crunches or regulatory deadline scrambles.
The outcome: DIFC-grade control with automation-scale efficiency. Better accuracy than manual processes, with complete human accountability.
Real Numbers: An investment Firm's 90-Day Transformation
Abstract explanations only go so far. Here's what actually happened when a mid-sized DIFC wealth advisory implemented AI agents.
The Firm
- AED 20M assets under management
- 65 high-net-worth clients
- 12-person team
- Typical mid-market wealth advisory profile
The Challenge
Client onboarding took 9 days due to manual KYC verification. Quarterly portfolio reporting required 10+ days of staff time. Client communication was reactive rather than proactive. The compliance team focused on data entry rather than strategic risk management.
Most critically: growth had stalled. Advisors couldn't handle additional clients without overwhelming back-office capacity.
The Implementation Timeline
Weeks 1–2: Assessment and workflow mapping. KYC and Portfolio Report agents configured and tested.
Weeks 3–4: KYC and reporting agents went live with pilot client subset. Staff trained on review and approval workflows.
Weeks 5–6: First DFSA filing completed using AI-assisted workflow. Compliance Filing agent deployed.
Weeks 7–8: Investor Communication agent added. Full integration completed across all client accounts.
The Measured Results
Onboarding efficiency:
- Time-to-activation reduced from 9 days to 3 days
- Client satisfaction with onboarding process improved markedly
Reporting transformation:
- Quarterly reporting cycle compressed from 10 days to 3 days
- Clients gained real-time dashboard access
- Reporting quality improved (fewer manual calculation errors)
Operational capacity:
- 45% reduction in overall back-office workload
- 2.5 FTE worth of capacity redeployed from admin to client-facing roles
Compliance performance:
- Zero DFSA inspection findings in first post-implementation audit
- Complete audit trails for all regulatory submissions
- Compliance team shifted focus from data entry to strategic oversight
Financial impact:
- AED 950K annual operational savings achieved
- 22% growth in managed accounts without additional hiring
- Payback on implementation investment: under 4 months
Managing Partner assessment: "Our compliance team now focuses on oversight, not data entry. We've freed up talent for client relationships, not paperwork."
The Compliance Question: DFSA Requirements and Data Sovereignty
For DIFC firms, regulatory compliance isn't negotiable. Any automation solution must align with DFSA requirements and UAE data sovereignty laws.
How AI Agents Align With DFSA Regulations
AML & GEN Modules:
Every client interaction flows through automated compliance checks. KYC data, STR flagging, CTR monitoring, and PEP tracking are logged with complete audit trails suitable for DFSA regulatory reviews. The difference from manual processes: more consistent application of rules and better documentation.
FATCA/CRS Compliance:
AI agents cross-verify nationality, tax ID numbers, and reporting thresholds against current IRS and OECD guidelines. Error-free submissions eliminate costly amendments and penalty risk. Humans still review classifications before finalization.
ESR Reporting:
Economic Substance Regulation compliance requires meticulous documentation of business activities and UAE substance. AI agents automate data population for entity-level reporting while compliance officers verify accuracy and completeness.
UAE Data Sovereignty: Where Data Lives Matters
This is non-negotiable for DIFC operations: client data must remain within UAE jurisdiction.
Properly implemented AI solutions operate on UAE-based encrypted cloud infrastructure. Client information never crosses international borders. All data processing occurs on UAE servers.
Key security architecture:
- Enterprise-grade encryption for all client and transaction data
- Multi-factor authentication with role-based access controls
- Complete activity logging for security audit purposes
- Zero cross-border data transfers
This isn't just best practice—it's regulatory compliance. DIFC firms need assurance that automation doesn't create data residency violations.
Common Questions From Investment Firm Managing Partners
"Will this replace our staff?"
No. AI agents augment professionals rather than replace them. Staff shift from tedious manual work to higher-value activities: strategic client advisory, exception handling, relationship development, and oversight.
Most firms redeploy freed capacity toward revenue-generating roles rather than reducing headcount. The advisor who spent 60% of her time on admin work now spends 80% on client strategy. The compliance analyst who manually populated forms now focuses on risk pattern analysis.
"How long does implementation actually take?"
Typical timeline is 90 days from initial setup to full deployment, using a phased approach:
- Days 1–30: Map workflows, deploy first two agents (KYC and reporting)
- Days 31–60: Add compliance and communication agents, pilot with client subset
- Days 61–90: Scale to full firm operations
The phased approach minimizes disruption. Initial pilots prove value before broad rollout.
"What happens if the AI makes a mistake?"
Human review catches it before any client impact or regulatory submission occurs. Remember: AI drafts, humans approve. Errors during automated extraction or draft generation get caught during human review—the same way a junior analyst's work gets reviewed by senior staff.
Error rates for AI-assisted processes are actually lower than fully manual workflows because AI doesn't get fatigued during repetitive tasks.
"Do we need to replace our existing systems?"
No. AI agents integrate with current technology stacks via APIs and data connectors. Whether you use Salesforce, Redtail, QuickBooks, or proprietary platforms, agents work within existing infrastructure. No platform migrations required.
"What's realistic ROI?"
Most investment firms achieve full payback within 4 months post-deployment. Annual operational savings typically range from AED 800K to AED 1M for mid-sized firms managing AED 300M–800M in AUM.
Revenue enablement benefits—increased advisor capacity, faster onboarding, improved client retention—compound over time and often exceed direct cost savings.
"Is this proven or experimental?"
The underlying technology (natural language processing, optical character recognition, machine learning) has been production-ready for years. What's new is application to DIFC-specific workflows with proper compliance architecture.
Multiple firms have completed implementations. The case study above isn't hypothetical—it's representative of actual results.
What This Means for Your Firm
The investment advisory industry in DIFC is bifurcating. One group of firms is achieving structural cost advantages, superior client experiences, and scalable growth trajectories. Another group is falling behind—not because of poor investment performance, but because operational inefficiency makes profitable growth impossible.
The firms pulling ahead aren't necessarily larger or better capitalized. They're simply rethinking how work gets done.
Three Strategic Implications
1. Cost structure becomes competitive advantage
When you operate with 40–50% lower back-office costs, you have strategic flexibility competitors don't: ability to serve smaller accounts profitably, capacity to invest in client experience, margin to weather market downturns.
2. Advisor productivity determines growth ceiling
If your advisors spend 60% of their time on administrative work, your growth is capacity-constrained. If they spend 80% on strategic client work, you can grow AUM without proportional staff increases. That's the difference between linear growth and scalable growth.
3. Client service expectations keep rising
Real-time portfolio access isn't a luxury anymore—it's table stakes. Firms delivering quarterly PDF reports are perceived as outdated. The gap between manual capabilities and client expectations will only widen.
The Window for Early-Mover Advantage
Right now, AI-augmented operations provide competitive differentiation. Within 18–24 months, they'll be baseline expectations. The firms implementing today establish market leadership. The firms waiting will scramble to catch up as competitors pull ahead.
This isn't about technology for technology's sake. It's about operational sustainability in an environment where regulatory obligations grow, talent costs rise, and client expectations outpace manual process capabilities.
Getting Started: What Assessment Looks Like
Understanding whether AI agents make sense for your specific firm requires honest assessment of current operations:
- How many hours monthly does your team spend on KYC, reporting, and compliance work?
- What percentage of advisor time goes to administrative tasks versus client advisory?
- Where do operational bottlenecks constrain your ability to take on new AUM?
- What compliance processes create the most risk exposure?
Mid sized firms with 8–25 staff typically see clear ROI. Smaller firms may not have sufficient workflow volume to justify implementation. Larger firms usually benefit significantly but require more complex integration.
A structured diagnostic—typically 2 weeks—maps current operations, quantifies automation potential, and provides specific ROI projections tailored to your firm's profile.
Conclusion
The question facing DIFC investment firms isn't whether to adopt AI automation—it's when and how.
The regulatory environment isn't getting simpler. Client expectations aren't moderating. Talent costs aren't decreasing. Manual processes that worked when you managed AED 20M won't scale to AED 100M or AED 1B.
AI agents aren't a silver bullet, but they're a proven tool for firms serious about operational sustainability. The technology works. The compliance architecture exists. The business case is demonstrable.
What matters now is understanding how it applies to your specific operations—and whether you're positioned to implement effectively.
The firms that figure this out in 2025 will have structural advantages their competitors can't easily replicate. The firms that wait will face harder choices in 2026 and beyond.
A comprehensive guide to understanding AI automation in DIFC-licensed investment advisory and wealth management operations
Your compliance officer just flagged another DFSA deadline. Your relationship managers are buried in quarterly reporting. Your operations team is manually reconciling custodian fees for the third time this week. And your best advisor just told you she spent six hours yesterday on administrative work instead of client meetings.
This isn't a staffing problem—it's a structural problem. And across DIFC, investment firms are discovering that the solution isn't hiring more people. It's fundamentally rethinking how work gets done.
Over the past 18 months, a quiet transformation has begun in Dubai's financial district. Mid-sized investment firms are achieving 40–50% reductions in back-office workload, cutting compliance exceptions by 70%, and recovering hundreds of hours monthly—not through harder work, but through AI agents purpose-built for financial operations.
This guide explains what's actually happening, how the technology works, and what it means for DIFC firms navigating rising regulatory complexity and client expectations that manual processes simply can't meet.
Table of Contents
1. Why DIFC Firms Are Hitting an Operational Ceiling
2. What AI Agents Actually Do (Without the Hype)
3. The Six Core Agents Transforming DIFC Operations
4. How Human-in-the-Loop Governance Works
5. Real Numbers: A DIFC Firm's 90-Day Transformation
6. The Compliance Question: DFSA Requirements and Data Sovereignty
7. Common Questions From DIFC Managing Partners
8. What This Means for Your Firm
Why DIFC Firms Are Hitting an Operational Ceiling
Three converging forces are squeezing DIFC investment firms simultaneously—and traditional solutions aren't working.
Force 1: Regulatory Workload Has Increased 40% Since 2021
DFSA's AML, GEN, and COB modules now require granular transaction tracing that didn't exist four years ago. ESR filings demand detailed documentation of economic substance. FATCA and CRS compliance require cross-border tax verification that changes annually.
The result: what used to be quarterly compliance work now requires continuous monitoring. Firms that managed regulatory obligations with one compliance analyst now need two or three—each costing AED 250K–350K annually.
Force 2: Back-Office Talent Is Expensive and Scarce
DIFC's talent market is competitive. Operations staff with financial services experience command premium salaries. Training new hires takes months. Turnover disrupts continuity.
The math doesn't work: as regulatory obligations grow, firms hire more back-office staff, leaving less budget for revenue-generating roles like business development and client relationship management. Growth stalls because operational costs consume margin.
Force 3: Client Service Expectations Have Fundamentally Shifted
83% of high-net-worth clients now expect real-time portfolio access. Quarterly PDF reports feel archaic. Clients want instant responses to questions about positions, performance, and market events.
Manual workflows can't deliver this. Excel-based reporting takes days or weeks. Email updates require staff time that doesn't scale. Firms lose competitive advantage to more digitally responsive competitors.
The Hidden Cost: 450 Hours Monthly Lost to Administrative Work
A typical 10-person DIFC investment firm loses 450–500 hours every month to non-revenue work:
- KYC and onboarding: 120+ hours collecting documents, verifying identities, checking FATCA/CRS classifications
- Investor reporting: 200+ hours per quarter extracting custodian data, reconciling positions, formatting reports
- Compliance filings: 80+ hours preparing DFSA submissions, maintaining AML registers, tracking deadlines
- Client communication: 60+ hours drafting updates, summarizing meetings, logging CRM activities
That's 2.5 full-time employees working exclusively on operational overhead. For most firms, that represents AED 900K–1.2M in annual labor costs that generate zero revenue and don't scale with AUM growth.
The operational ceiling: advisors can't take on more clients because they're drowning in administrative work for existing ones.
What AI Agents Actually Do (Without the Hype)
Strip away the marketing language, and AI agents are specialized software applications that handle specific, repetitive business workflows autonomously.
Think of them as exceptionally capable junior analysts who never sleep, never make transcription errors, and cost a fraction of human labor. They don't replace professional judgment—they eliminate the grunt work that buries professionals.
How They're Different From Traditional Automation
Traditional robotic process automation (RPA) follows rigid, pre-programmed rules. If a form changes or data appears in an unexpected format, the automation breaks.
AI agents adapt. They interpret unstructured data—scanned passports, email threads, PDF bank statements—and extract relevant information regardless of format variations. They understand context the way humans do, but process it at machine speed.
Example: A traditional RPA bot extracts a client name from a KYC form—but only if the name appears in the exact expected location. An AI agent extracts the name from any document type (passport, utility bill, bank statement) because it understands what "client name" conceptually means.
The Critical Difference: Human-in-the-Loop Architecture
Here's what matters for investment firms: properly designed AI agents don't make final decisions. They draft, suggest, and flag—but humans review and approve.
The AI extracts KYC data from a scanned Emirates ID. A human verifies it's correct before the client record is created. The AI drafts a compliance filing. A compliance officer reviews and approves before submission. The AI generates a portfolio report. An advisor confirms accuracy before client delivery.
This architecture preserves professional accountability while eliminating manual drudgery. The compliance officer's name is on the filing, not the AI's. The advisor owns the client relationship, not the software.
For regulatory purposes, this matters enormously. DFSA inspectors don't audit AI decisions—they audit human decisions supported by AI tools. The audit trail shows what the AI suggested and what the human approved.
The Six Core Agents Transforming investment Operations
Different workflows require different capabilities. Here's what each agent actually does and the problems it solves.
1. KYC & Onboarding Agent
What it does: Extracts information from scanned documents (passports, Emirates IDs, utility bills), validates FATCA classifications against IRS guidelines, verifies CRS tax residency, and populates CRM fields automatically.
The manual alternative: Staff manually type client information from documents into multiple systems, cross-reference tax classifications in PDF rulebooks, and verify addresses against utility bills—9–10 days from inquiry to account activation.
Outcome: Onboarding compressed to 3 days. Firms report 30–50% faster time-to-revenue for new client relationships.
2. Compliance Filing Agent
What it does: Monitors regulatory deadlines, pre-populates DFSA filing templates with data from internal systems, maintains AML registers with automatic transaction flagging, and sends proactive alerts when submissions approach due dates.
The manual alternative: Compliance analysts manually gather transaction data from multiple systems, populate regulatory templates field-by-field, cross-reference internal records, and calendar deadline reminders.
Outcome: Approximately 70% fewer compliance exceptions. Near-elimination of late filing penalties.
3. Fee & Reconciliation Agent
What it does: Matches advisory fee invoices against services rendered, reconciles custodian fee statements against internal billing records, and flags discrepancies for immediate review.
The manual alternative: Operations staff manually compare line items across Excel spreadsheets, investigate breaks, and resolve billing disputes that arise from reconciliation errors.
Outcome: Near-zero reconciliation breaks and dramatic reduction in client billing disputes.
4. Portfolio Report Generator
What it does: Pulls position data from multiple custodian platforms, calculates performance attribution and risk metrics, generates branded PDF reports, and creates interactive Power BI dashboards with real-time data.
The manual alternative: Staff manually extract data from custodian websites, consolidate positions in Excel, calculate returns manually, format reports in Word or PowerPoint—10+ days per quarterly cycle.
Outcome: Reporting cycles shrink from 10 days to 3 days. Clients gain 24/7 dashboard access to current positions.
5. Investor Communication Agent
What it does: Summarizes lengthy email threads into concise bullet points, drafts proactive client update messages based on portfolio events, and suggests personalized insights based on client history.
The manual alternative: Relationship managers read through multi-threaded email conversations, manually draft updates for each client, and struggle to maintain communication consistency across growing client bases.
Outcome: Advisors report 15–20% increase in AUM productivity through time savings. Client satisfaction scores improve measurably.
6. Meeting Summary Agent
What it does: Extracts key decisions and action items from Teams/Zoom meeting transcripts, automatically syncs tasks to CRM with assigned owners and due dates, and distributes follow-up summaries to participants within minutes.
The manual alternative: Someone manually takes meeting notes, types up summaries after the call, and manually creates CRM tasks—hoping nothing important gets missed.
Outcome: Elimination of "dropped ball" scenarios where commitments fall through cracks. Improved client trust and satisfaction.
How Human-in-the-Loop Governance Actually Works
The biggest concern most investment firms have about AI isn't capability—it's accountability. Who's responsible when something goes wrong?
The answer is straightforward: the same people who are responsible now. AI agents don't change accountability—they change what professionals spend time doing.
The Four-Layer Control Framework
Layer 1: AI Executes Defined Tasks
AI agents handle data extraction, document drafting, formatting, pattern recognition, and preliminary analysis. They work at machine speed within carefully defined boundaries.
Layer 2: Human Verifies and Approves
Every client-facing communication and every compliance submission requires explicit human approval. AI drafts; humans review, edit if necessary, and approve. Professional judgment remains exactly where it's always been.
Layer 3: All Actions Logged
Every AI action is timestamped and stored in immutable audit trails. DFSA inspectors can review exactly what the AI did, when it did it, and who approved it. This documentation is actually superior to manual processes, where actions often go unrecorded.
Layer 4: Quarterly Accuracy Audits
Regular reviews ensure AI performance remains within acceptable parameters. Error rates are tracked, and models are refined when performance drifts.
Error Rates: AI-Assisted vs. Fully Manual
Independent testing shows that properly supervised AI agents achieve error rates of 0.1–0.3% on structured tasks like data extraction and compliance checks.
Fully manual human processes typically produce error rates of 2–5% due to fatigue, distraction, and time pressure—particularly during quarter-end reporting crunches or regulatory deadline scrambles.
The outcome: DIFC-grade control with automation-scale efficiency. Better accuracy than manual processes, with complete human accountability.
Real Numbers: An investment Firm's 90-Day Transformation
Abstract explanations only go so far. Here's what actually happened when a mid-sized DIFC wealth advisory implemented AI agents.
The Firm
- AED 20M assets under management
- 65 high-net-worth clients
- 12-person team
- Typical mid-market wealth advisory profile
The Challenge
Client onboarding took 9 days due to manual KYC verification. Quarterly portfolio reporting required 10+ days of staff time. Client communication was reactive rather than proactive. The compliance team focused on data entry rather than strategic risk management.
Most critically: growth had stalled. Advisors couldn't handle additional clients without overwhelming back-office capacity.
The Implementation Timeline
Weeks 1–2: Assessment and workflow mapping. KYC and Portfolio Report agents configured and tested.
Weeks 3–4: KYC and reporting agents went live with pilot client subset. Staff trained on review and approval workflows.
Weeks 5–6: First DFSA filing completed using AI-assisted workflow. Compliance Filing agent deployed.
Weeks 7–8: Investor Communication agent added. Full integration completed across all client accounts.
The Measured Results
Onboarding efficiency:
- Time-to-activation reduced from 9 days to 3 days
- Client satisfaction with onboarding process improved markedly
Reporting transformation:
- Quarterly reporting cycle compressed from 10 days to 3 days
- Clients gained real-time dashboard access
- Reporting quality improved (fewer manual calculation errors)
Operational capacity:
- 45% reduction in overall back-office workload
- 2.5 FTE worth of capacity redeployed from admin to client-facing roles
Compliance performance:
- Zero DFSA inspection findings in first post-implementation audit
- Complete audit trails for all regulatory submissions
- Compliance team shifted focus from data entry to strategic oversight
Financial impact:
- AED 950K annual operational savings achieved
- 22% growth in managed accounts without additional hiring
- Payback on implementation investment: under 4 months
Managing Partner assessment: "Our compliance team now focuses on oversight, not data entry. We've freed up talent for client relationships, not paperwork."
The Compliance Question: DFSA Requirements and Data Sovereignty
For DIFC firms, regulatory compliance isn't negotiable. Any automation solution must align with DFSA requirements and UAE data sovereignty laws.
How AI Agents Align With DFSA Regulations
AML & GEN Modules:
Every client interaction flows through automated compliance checks. KYC data, STR flagging, CTR monitoring, and PEP tracking are logged with complete audit trails suitable for DFSA regulatory reviews. The difference from manual processes: more consistent application of rules and better documentation.
FATCA/CRS Compliance:
AI agents cross-verify nationality, tax ID numbers, and reporting thresholds against current IRS and OECD guidelines. Error-free submissions eliminate costly amendments and penalty risk. Humans still review classifications before finalization.
ESR Reporting:
Economic Substance Regulation compliance requires meticulous documentation of business activities and UAE substance. AI agents automate data population for entity-level reporting while compliance officers verify accuracy and completeness.
UAE Data Sovereignty: Where Data Lives Matters
This is non-negotiable for DIFC operations: client data must remain within UAE jurisdiction.
Properly implemented AI solutions operate on UAE-based encrypted cloud infrastructure. Client information never crosses international borders. All data processing occurs on UAE servers.
Key security architecture:
- Enterprise-grade encryption for all client and transaction data
- Multi-factor authentication with role-based access controls
- Complete activity logging for security audit purposes
- Zero cross-border data transfers
This isn't just best practice—it's regulatory compliance. DIFC firms need assurance that automation doesn't create data residency violations.
Common Questions From Investment Firm Managing Partners
"Will this replace our staff?"
No. AI agents augment professionals rather than replace them. Staff shift from tedious manual work to higher-value activities: strategic client advisory, exception handling, relationship development, and oversight.
Most firms redeploy freed capacity toward revenue-generating roles rather than reducing headcount. The advisor who spent 60% of her time on admin work now spends 80% on client strategy. The compliance analyst who manually populated forms now focuses on risk pattern analysis.
"How long does implementation actually take?"
Typical timeline is 90 days from initial setup to full deployment, using a phased approach:
- Days 1–30: Map workflows, deploy first two agents (KYC and reporting)
- Days 31–60: Add compliance and communication agents, pilot with client subset
- Days 61–90: Scale to full firm operations
The phased approach minimizes disruption. Initial pilots prove value before broad rollout.
"What happens if the AI makes a mistake?"
Human review catches it before any client impact or regulatory submission occurs. Remember: AI drafts, humans approve. Errors during automated extraction or draft generation get caught during human review—the same way a junior analyst's work gets reviewed by senior staff.
Error rates for AI-assisted processes are actually lower than fully manual workflows because AI doesn't get fatigued during repetitive tasks.
"Do we need to replace our existing systems?"
No. AI agents integrate with current technology stacks via APIs and data connectors. Whether you use Salesforce, Redtail, QuickBooks, or proprietary platforms, agents work within existing infrastructure. No platform migrations required.
"What's realistic ROI?"
Most investment firms achieve full payback within 4 months post-deployment. Annual operational savings typically range from AED 800K to AED 1M for mid-sized firms managing AED 300M–800M in AUM.
Revenue enablement benefits—increased advisor capacity, faster onboarding, improved client retention—compound over time and often exceed direct cost savings.
"Is this proven or experimental?"
The underlying technology (natural language processing, optical character recognition, machine learning) has been production-ready for years. What's new is application to DIFC-specific workflows with proper compliance architecture.
Multiple firms have completed implementations. The case study above isn't hypothetical—it's representative of actual results.
What This Means for Your Firm
The investment advisory industry in DIFC is bifurcating. One group of firms is achieving structural cost advantages, superior client experiences, and scalable growth trajectories. Another group is falling behind—not because of poor investment performance, but because operational inefficiency makes profitable growth impossible.
The firms pulling ahead aren't necessarily larger or better capitalized. They're simply rethinking how work gets done.
Three Strategic Implications
1. Cost structure becomes competitive advantage
When you operate with 40–50% lower back-office costs, you have strategic flexibility competitors don't: ability to serve smaller accounts profitably, capacity to invest in client experience, margin to weather market downturns.
2. Advisor productivity determines growth ceiling
If your advisors spend 60% of their time on administrative work, your growth is capacity-constrained. If they spend 80% on strategic client work, you can grow AUM without proportional staff increases. That's the difference between linear growth and scalable growth.
3. Client service expectations keep rising
Real-time portfolio access isn't a luxury anymore—it's table stakes. Firms delivering quarterly PDF reports are perceived as outdated. The gap between manual capabilities and client expectations will only widen.
The Window for Early-Mover Advantage
Right now, AI-augmented operations provide competitive differentiation. Within 18–24 months, they'll be baseline expectations. The firms implementing today establish market leadership. The firms waiting will scramble to catch up as competitors pull ahead.
This isn't about technology for technology's sake. It's about operational sustainability in an environment where regulatory obligations grow, talent costs rise, and client expectations outpace manual process capabilities.
Getting Started: What Assessment Looks Like
Understanding whether AI agents make sense for your specific firm requires honest assessment of current operations:
- How many hours monthly does your team spend on KYC, reporting, and compliance work?
- What percentage of advisor time goes to administrative tasks versus client advisory?
- Where do operational bottlenecks constrain your ability to take on new AUM?
- What compliance processes create the most risk exposure?
Mid sized firms with 8–25 staff typically see clear ROI. Smaller firms may not have sufficient workflow volume to justify implementation. Larger firms usually benefit significantly but require more complex integration.
A structured diagnostic—typically 2 weeks—maps current operations, quantifies automation potential, and provides specific ROI projections tailored to your firm's profile.
Conclusion
The question facing DIFC investment firms isn't whether to adopt AI automation—it's when and how.
The regulatory environment isn't getting simpler. Client expectations aren't moderating. Talent costs aren't decreasing. Manual processes that worked when you managed AED 20M won't scale to AED 100M or AED 1B.
AI agents aren't a silver bullet, but they're a proven tool for firms serious about operational sustainability. The technology works. The compliance architecture exists. The business case is demonstrable.
What matters now is understanding how it applies to your specific operations—and whether you're positioned to implement effectively.
The firms that figure this out in 2025 will have structural advantages their competitors can't easily replicate. The firms that wait will face harder choices in 2026 and beyond.