AI Agents: Reshaping Insurance in the UAE and the GCC
AI agents are fundamentally defined as sophisticated software programs or systems designed to autonomously perceive their environment, process information, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals [Pre-computation].
This capability marks a significant evolution from simpler interfaces like chatbots, which primarily respond to user queries based on scripts. The increasing power of large language models (LLMs) is enabling AI agents to reach their full potential, proving to be practical tools that can contribute significantly to value-driving AI systems across various industries, including the general insurance sector.
This article will delve into the profound impact of AI agents on the general insurance industry, highlighting their key principles and features as applied across the value chain, from insurance companies to brokers, reinsurers, and other ancillary services. It will also bring in elements specific to the UAE and GCC regions, recognizing their unique market dynamics and accelerating digital transformation.
Key Principles and Features of AI Agents in General Insurance
The intelligent operation of AI agents is underpinned by several core principles and features, which, when applied to the general insurance industry, drive efficiency, improve accuracy, enable personalization, and enhance customer experience.
1. Perception (Observing/Sensing):
At the foundational level, AI agents gather information from their surroundings through various "sensors" or data collection mechanisms. In the general insurance context, this translates to perceiving a wide array of data. This raw input can involve parsing text commands from customer inquiries, analyzing vast streams of policy and claims data, interpreting images of damaged property, or monitoring real-time market trends. For instance, a robotic AI agent might use cameras and radar to detect objects, while a chatbot processes user input or searches knowledge bases. This diverse input is then converted into a format the agent can understand and process, forming the basis for subsequent decision-making.
2. Reasoning and Decision-Making/Planning:
Following perception, AI agents analyze the gathered information to make informed decisions. This is a core cognitive process that involves interpreting complex datasets, drawing inferences, predicting future outcomes, and selecting the most appropriate response or action based on their programming and current context. In insurance, this could manifest as an agent interpreting complex claims data to assess liability, predicting the likelihood of fraud, or planning optimal pricing strategies for a new policy. Advanced agents can generate possible actions, assess potential outcomes, and plan sequences of actions to achieve desired results. They leverage machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to evaluate inputs against their objectives, perform sentiment analysis on customer feedback, and use classification algorithms to categorize inquiries or claims.
For example, Decision AI is specifically designed to make business decisions from data, processing diverse data sources like text, images, and structured data to enable rapid, data-driven, and precise decisions. It can automate up to 97% of knowledge tasks, accelerate decision-making, and support scalability.
3. Action Execution: Once a decision is made, AI agents execute tasks through their output interfaces. This translates decisions into real-world actions. In the insurance domain, these actions can include generating text responses to customer queries, updating policy databases, triggering automated workflows for claims processing, sending commands to other internal or external systems (like payment gateways or repair shops), or even physical actions if the agent is embodied (e.g., a robot inspecting damage). The action module ensures the chosen response is properly formatted and delivered.
4. Autonomy: A defining characteristic of AI agents is their high degree of autonomy, enabling them to operate and make decisions independently to achieve goals without constant human prompting or intervention. This "agentic artificial intelligence empowers the autonomy of modern enterprises". For example, an AI agent in a contact center can automatically ask customers questions, look up information, and respond with solutions, determining independently if it can resolve a query or needs to escalate it to a human. This capability means agents can monitor data streams, automate complex workflows, and execute tasks autonomously.
5. Goal-Oriented: AI agents are fundamentally designed to pursue specific goals and complete tasks on behalf of users. Humans typically set these goals, but the agent independently chooses the best actions to achieve them. They evaluate different actions to find those that best move them closer to their defined goals. Examples include logistics routing agents finding optimal delivery routes or smart heating systems planning temperature adjustments to reach desired comfort levels efficiently.
6. Learning and Adaptability (Self-refining): Advanced AI agents can improve their behavior over time based on experience and feedback. They analyze the outcomes of their actions, update their knowledge bases, and refine their decision-making processes, often using machine learning techniques like reinforcement learning. This allows them to "continuously optimize their responses because they learn with every interaction". They can also be considered "predictive agents" since they use historical data and current trends to anticipate future events or outcomes and adjust their actions to enhance future performance. A customer service chatbot, for instance, can improve response accuracy over time by learning from previous interactions.
7. Knowledge Management/Memory: Agents maintain and use knowledge bases containing domain-specific information, learned patterns, and operational rules. They are equipped with various types of memory, including short-term for immediate interactions, long-term for historical data and conversations, episodic for past interactions, and consensus memory for shared information among agents. They can dynamically access and incorporate relevant information, often through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), to form accurate and contextual responses. For example, a customer support agent might use RAG to pull information from product documentation, past cases, and company policies.
8. Tool Use: AI agents can utilize functions or external resources (tools) to interact with their environment and enhance their capabilities. This enables them to perform complex tasks by accessing information, manipulating data, or controlling external systems. Examples include connecting to payment gateways, accessing external databases, or generating reports.
9. Handling Complexity: AI agents excel at managing complex, dynamic tasks, seamlessly understanding context, and handling nuanced inquiries. They are designed to manage multi-step troubleshooting efficiently and precisely. This level of sophistication distinguishes them from simpler systems that are limited to straightforward, repetitive tasks.
10. Collaboration (Multi-Agent Systems - MAS): Some AI agents are designed to work effectively with other AI agents (and sometimes humans) to achieve a common goal. This requires communication, coordination, and shared understanding, enabling them to tackle more complex, interdependent workflows. MAS can be cooperative, where agents share information and resources to achieve common goals, or competitive, where agents compete for resources following defined rules.
11. Scalability: AI agents can handle large volumes of tasks simultaneously, making them ideal for scaling operations. Multi-agent systems, for instance, are scalable and well-suited for tasks requiring dynamic responses to varied inputs.
These principles are largely enabled by underlying technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs), which serve as the "brain" for modern AI agents, providing the ability to understand, reason, and act by processing multimodal information (text, voice, video, audio, code) simultaneously.
AI Agents Across the General Insurance Value Chain: UAE and GCC Context
The general insurance market in the UAE and GCC is experiencing significant growth, driven by digital transformation initiatives, evolving regulatory landscapes, and increasing demand for personalized and efficient services. In this dynamic environment, AI agents are not just a technological advancement but a strategic imperative for companies seeking to gain a competitive edge.
Insurance Companies and application of AI Agents
For insurance companies in the UAE and GCC, AI agents are on the verge of revolutionizing core operations, from policy inception to claims settlement.
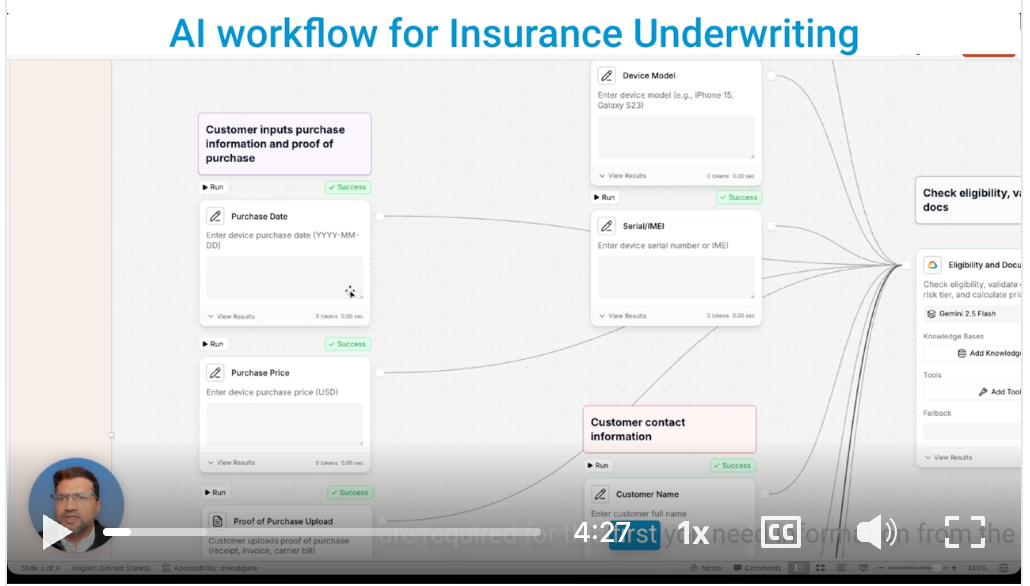
• Underwriting and Risk Assessment: This is a crucial area where AI agents offer substantial value.
Decision AI can process diverse data sources—including text from financial reports, images from property assessments, and structured data from credit scores—to rapidly assess risk and provide precise policy recommendations. For example, in motor insurance, a Decision AI agent could analyze driving behavior data (from telematics, external detail: often popular in UAE/GCC for usage-based insurance), past accident claims, and vehicle specifications to calculate a highly personalized premium.
Utility-based agents are invaluable here, as they can evaluate investments based on factors like risk, return, and diversification, choosing options that provide the most value. This allows for optimal pricing that balances profitability for the insurer with competitive rates for the customer.
Furthermore, Learning agents can continuously refine risk models based on new data and claim outcomes, ensuring that underwriting decisions become increasingly accurate and adaptive over time. This allows insurers to predict events and outcomes, adjusting actions to enhance future performance.
• Policy Issuance and Management: Automating policy issuance and amendments significantly accelerates turnaround times.
Document AI is central to this, automating complex document workflows by leveraging NLP and ML to autonomously read, interpret, categorize, and validate high volumes of documents. For instance, it can extract critical information from new policy applications, validate entries against predefined rules, detect inconsistencies, and efficiently route documents to the next step, triggering follow-up actions when needed. This adaptive AI improves over time with diverse data formats and document types, ensuring fast and error-free processing essential for industries like finance and insurance.
Simple reflex agents can also be deployed to automatically send acknowledgment emails to policyholders upon receiving a claim submission or policy request, ensuring immediate customer communication.
• Claims Processing: The claims process is often a bottleneck in the insurance value chain, but AI agents streamline it significantly.
Document AI can efficiently extract key information from claim forms, damage reports, and medical documents.
Decision AI then processes these claims, autonomously assessing risk, and providing recommendations based on real-time data and historical patterns.
Data agents handle large-scale data processing tasks, from cleaning to analytics, extracting insights from massive datasets to help businesses make data-driven decisions quickly. This enables faster and more accurate claims adjudication, reducing manual effort and processing time. For instance, in health insurance claims prevalent in the UAE, AI agents can process medical bills, prescriptions, and diagnosis reports to verify coverage and calculate payouts with high accuracy.
• Customer Service: The demand for instant, personalized customer service is high in the UAE/GCC, and AI agents are ideal for meeting this expectation.
Customer agents are designed to engage with users, answer inquiries, and handle routine customer service tasks, usually 24/7. Equipped with Conversational AI and NLP, these agents can communicate in a natural, conversational manner, providing seamless support and improving customer satisfaction. They can handle billing inquiries, product troubleshooting, and even route complex issues to live agents or escalate to specialized teams.
Learning agents enhance chatbots by refining product suggestions based on user interactions and preferences, and improving response accuracy over time.
• Fraud Detection:
Fraud remains a significant challenge for insurers globally, and in the GCC, AI agents are critical for bolstering defenses.
Security agents continuously monitor systems, detect anomalies, and respond to threats in real-time. They leverage AI to detect fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns in customer behavior, instantly flagging and blocking suspicious activity, protecting accounts, and reducing fraud losses. Simple reflex agents can immediately flag transactions that meet predefined criteria for potential fraud. Learning agents further enhance these capabilities by refining their detection models based on new fraud patterns and historical data.
• Marketing and Personalization:
AI agents can significantly enhance marketing efforts by enabling hyper-personalization. Learning agents power recommendation engines that refine product suggestions (e.g., insurance policies) based on user interactions and preferences. This leads to personalized experiences that account for individual factors or preferences, such as suggested products based on past purchases or browsing history.
Creative agents can assist marketing teams by drafting social media posts, generating ad copy, or designing basic graphics that adhere to brand guidelines, allowing creative teams to focus on higher-level strategy.
• Compliance and Regulatory Adherence:
The UAE and GCC insurance markets are subject to evolving regulations.
Data agents and Document AI are crucial for ensuring compliance by processing vast datasets and documents to identify patterns, extract insights, and generate compliance reports accurately and efficiently. This helps insurers stay ahead of regulatory changes and avoid penalties.
Insurance Brokers
Insurance brokers in the UAE and GCC, who act as intermediaries between clients and insurers, can leverage AI agents to enhance their service delivery and operational efficiency.
• Client Acquisition and Management:
Customer agents can handle initial client inquiries, provide basic information on policy types, and qualify leads, operating 24/7.
Database AI is particularly beneficial for brokers, as it optimizes database management, querying, and analysis with minimal user input. Equipped with natural language understanding, it makes databases accessible to non-technical users (e.g., sales representatives), allowing them to query client data or policy information in simple, everyday language. This enhances the speed and accuracy of query responses and improves customer satisfaction.
• Policy Comparison and Recommendation: Brokers often need to compare multiple policies from different insurers to find the best fit for their clients.
Utility-based agents are perfectly suited for this, evaluating various policies based on client needs, risk profiles, price, coverage options, and even specific Sharia-compliant requirements (for Takaful insurance, external detail: specific to Islamic finance in the region) to find the optimal solution. These agents can quickly process vast amounts of policy data and present the most beneficial options.
• Customer Support: Conversational AI transforms customer interactions by providing responsive, natural language support that enhances the user experience. Brokers can use these agents to answer client inquiries about policy details, assist with claims submission, or provide personalized recommendations in real-time.
• Workflow Automation: Beyond client-facing roles, AI agents can automate a myriad of administrative tasks for brokers, such as data entry, document preparation, and follow-up communications, significantly increasing efficiency and freeing up human resources for more strategic client advisory roles.
Reinsurers and use of AI Agents
Reinsurers, who act as insurers for insurance companies, also stand to gain immensely from AI agent capabilities, particularly in complex risk analysis and portfolio management.
• Risk Portfolio Analysis: Reinsurers deal with aggregated risks from multiple primary insurers.
Data agents are crucial here for large-scale data processing, enabling the extraction of deep insights from massive datasets for comprehensive risk assessment.
Decision AI can further assess the aggregated risk and provide recommendations based on real-time data and extensive historical patterns, aiding in crucial underwriting decisions for reinsurance treaties.
• Catastrophe Modeling and Prediction: Reinsurers rely heavily on accurate catastrophe modeling.
Learning agents and predictive agents use historical data and current trends to anticipate future events and outcomes, refining their models over time to provide more accurate predictions for natural disasters, major industrial accidents, or even large-scale cyberattacks. This allows reinsurers to better manage their exposure and allocate capital effectively.
• Automated Quoting and Capacity Management: For complex reinsurance deals, Goal-based agents and Utility-based agents can optimize quoting processes by evaluating various factors like the primary insurer's portfolio characteristics, historical losses, current market conditions, and the reinsurer's capacity and risk appetite. These agents can propose optimal pricing and terms that maximize utility (e.g., profitability and risk diversification) for the reinsurer.
• Claims Reserving and Loss Adjusting: Reinsurers need precise loss reserving to manage their liabilities.
Data agents can process vast amounts of historical claims data, including complex loss adjustment expenses and subrogation recoveries, to provide highly accurate reserving estimates. This enhances financial stability and decision-making for future capital allocation.
Other Parts of the Insurance Value Chain
The impact of AI agents extends to other crucial parts of the insurance ecosystem, including insurtech startups, third-party administrators (TPAs), and loss adjusters.
• AI-driven Process Automation (General): Platforms like AgentFlow provide an all-in-one Agentic AI platform for finance and insurance, designed to automate end-to-end workflows securely for faster turnaround. This enables enhanced operational efficiency across the entire value chain.
• Unstructured Data Processing: Insurance inherently involves a large volume of unstructured data (e.g., claim reports, medical records, police reports, correspondence). Unstructured AI tackles this complexity by converting various document types (PDFs, HTML, Excel) into structured, AI-ready formats. This "ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) layer" is essential for businesses needing to process non-standardized data for downstream AI applications like Document AI and Conversational AI, providing actionable insights from raw information. This is particularly relevant in the UAE/GCC where diverse document formats from various jurisdictions might be encountered.
• Report Generation: For loss adjusters, TPAs, and internal departments, Report AI can generate ready-to-publish content, from detailed assessment reports to summary overviews. This capability significantly reduces the time spent on manual reporting, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
• Code Agents: For insurtechs and internal IT departments across the insurance sector, code agents assist software developers in creating and maintaining applications and systems. They streamline tasks like detecting and resolving bugs, recommending code optimizations, and generating code snippets from natural language inputs, thereby enhancing code quality and speeding up the development lifecycle. This is crucial for rapid innovation and custom solution development in a competitive market.
• Security Agents: Given the sensitive nature of financial and personal data handled by all entities in the insurance value chain, security agents are paramount. They continuously monitor systems to detect anomalies and respond to threats in real-time, leveraging AI to enhance organizational security, safeguard sensitive data, and effectively mitigate risks. This includes detecting fraudulent activities, protecting accounts, and reducing fraud losses.
Local Context: UAE and GCC General Insurance Market
The UAE and wider GCC region present a fertile ground for AI adoption in general insurance due to several unique market dynamics and drivers.
• Market Dynamics: The GCC insurance market is characterized by rapid growth, increasing competition, and a strong drive towards digital transformation. Governments and private entities in the UAE and Saudi Arabia, for instance, are heavily investing in smart city initiatives and technological infrastructure, creating an environment ripe for AI adoption. There is a high level of digital literacy and expectation among consumers in these regions for seamless, technology-driven services.
Drivers for AI Adoption in UAE/GCC Insurance:
◦ Competitive Landscape: The burgeoning number of local and international insurers, brokers, and insurtechs in the UAE and GCC intensifies competition. AI agents offer a crucial differentiator by enabling cost reduction, increased efficiency, and superior customer experiences.
◦ Evolving Customer Expectations: Consumers in the UAE and GCC are increasingly tech-savvy and demand instant, personalized services across digital channels. AI agents meet this demand by providing 24/7 support, personalized recommendations, and expedited claims processing.
◦ Regulatory Environment: While general principles of AI apply, the regulatory bodies in the UAE and GCC are actively promoting innovation while ensuring consumer protection and data security. The need for improved accuracy in data-driven decisions, transparency in AI operations, and adherence to data privacy regulations is paramount. AI agents can assist in maintaining compliance by consistently applying rules and processing large volumes of regulatory documents.
◦ Talent Shortage: Like many rapidly growing sectors, the insurance industry in the GCC faces challenges in attracting and retaining specialized talent. Automation through AI agents can address human resource gaps by taking over repetitive tasks, freeing up human staff to focus on more complex, strategic, and value-added activities.
◦ Data Availability: The region generates vast amounts of customer, policy, and claims data, which is an ideal feedstock for AI analysis. Leveraging this data with AI agents allows for richer insights and more informed decision-making.
Specific AI Agent Applications (UAE/GCC Relevance):
◦ Motor Insurance: Given the high vehicle ownership and traffic volumes, motor insurance is a key segment. Utility-based agents can leverage telematics data (from vehicle sensors) to provide highly personalized, usage-based insurance pricing, optimizing for factors like safety and fuel efficiency (this is a common application of AI in motor insurance, external detail: widely adopted globally and gaining traction in the UAE). Simple reflex agents and security agents play a vital role in real-time fraud detection related to motor claims, analyzing patterns of behavior and quickly flagging suspicious activities.
◦ Health Insurance: With mandatory health insurance in many GCC countries, the volume of claims is immense. Learning agents can analyze patient data to create personalized treatment plans and provide predictive diagnostics, enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. Document AI and Decision AI are crucial for streamlining the processing of vast numbers of health claims and medical documents.
◦ Property & Casualty Insurance: As new smart cities and large infrastructure projects develop across the GCC, property and casualty insurance becomes more complex. Model-based reflex agents can be deployed in smart homes and buildings for enhanced security systems, distinguishing between routine activities and potential threats. The concept of Multi-agent systems for smart city traffic management systems, which regulate traffic flow and suggest alternative routes, directly correlates with large-scale urban development in the region. Siemens' Building X, using AI for smart building management, provides a clear example of AI agents optimizing complex environments like those found in mega-projects across the UAE.
◦ Sharia-compliant Insurance (Takaful): (This is an external concept, not directly from sources, but relevant to the region). In the Takaful sector, AI agents can be designed to ensure compliance with Sharia principles by analyzing transactions and operational processes, ensuring transparency and ethical adherence in financial products. This requires careful design to integrate the utility functions of agents with the ethical guidelines of Islamic finance.
Challenges and Considerations for AI Adoption in UAE/GCC Insurance
Despite the immense potential, deploying AI agents in the general insurance industry within the UAE and GCC comes with its own set of challenges. Organizations must address these concerns for successful and sustainable implementation.
• Computational Costs and Resources: Developing and operating advanced AI agents, especially those leveraging deep learning, demands significant computing power, storage, and memory resources. This requires substantial upfront investments in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance, alongside the need for specialized staff. Organizations must carefully plan their deployments, often considering cloud-based solutions like AWS or Google Cloud to scale resources flexibly.
• Human Training and Oversight: While AI agents operate autonomously, they require human training and general oversight to ensure models operate properly, are accurately calibrated, and are continuously updated. This necessitates access to large volumes of quality data and a cadre of trained professionals who understand how to develop, calibrate, and refine AI models. Building this talent pool within the UAE and GCC is a continuous effort.
• Integration Difficulties: Not all AI agent types are inherently designed to work together seamlessly in hybrid or multi-agent systems, nor do they always integrate easily with existing legacy systems prevalent in some insurance operations. Careful planning and testing are required before deployment to avoid costly mistakes or interoperability errors.
• Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns: The deployment of AI agents involves collecting, storing, and processing massive volumes of sensitive customer and claims data. Organizations in the UAE and GCC must navigate stringent data privacy requirements and implement robust measures to improve data security posture. Moreover, advanced deep learning models may inadvertently produce unfair, biased, or inaccurate results if trained on biased data. Ensuring fairness, transparency in decision-making, and applying safeguards such as human reviews are crucial for ethical deployment and maintaining trust with customers. The unique cultural and legal norms of the GCC region add another layer of complexity to these ethical considerations.
• Infinite Loops and Overfitting: AI agents, particularly simple reflex agents in partially observable environments, may encounter "infinite loops" where they get stuck in endless action cycles. Learning agents also face the risk of "overfitting" data, performing well in known scenarios but poorly in unseen or novel situations. Balancing the specificity of training with the need for generalizability is a continuous challenge.
Conclusion
The world of AI agents is vast, continuously evolving, and holds immense potential to transform the general insurance industry in the UAE and GCC. From fundamental principles like perception and reasoning to advanced capabilities like learning, tool use, and multi-agent collaboration, AI agents are revolutionizing how insurance companies, brokers, reinsurers, and ancillary service providers operate.
By automating complex, repetitive tasks, enabling real-time data-driven decisions, scaling operations, and enhancing personalized customer experiences, AI agents offer profound benefits such as increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and significant cost savings.
The agility and problem-solving capabilities of AI agents are well-suited to the dynamic and competitive insurance landscape of the UAE and GCC, promising faster turnaround times, more precise risk assessments, and streamlined claims processes.
However, realizing this potential requires a strategic approach that addresses the inherent challenges. Organizations must be prepared for significant computational investments, commit to human training and oversight, manage complex integrations, and rigorously ensure data privacy and ethical AI deployment. By carefully assessing their specific needs and goals, evaluating available AI agent types (from simple reflex to sophisticated hybrid models), and implementing robust governance frameworks, businesses in the UAE and GCC general insurance sector can unlock unparalleled opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and growth.
The path forward involves embracing these intelligent systems to work alongside humans in ways that are increasingly sophisticated, reshaping the future of insurance in the region.