AI Agents: A comprehensive briefing
Executive Summary
AI agents are autonomous software programs designed to perceive their environment, process information, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific, human-defined goals. Unlike traditional software or basic chatbots, AI agents possess varying degrees of autonomy, learning capabilities, and problem-solving skills, allowing them to handle complex, dynamic tasks without constant human intervention. Their capabilities are significantly enhanced by advancements in large language models (LLMs) and generative AI, enabling them to process multimodal information, reason, learn, and adapt over time. The widespread adoption of AI agents is driven by their ability to increase efficiency, improve accuracy, enable personalization, and drive cost savings across diverse industries.
1. What are AI Agents?
An AI agent is an autonomous entity that perceives its environment, processes information, and takes actions to achieve specific goals. They are sophisticated software programs that go beyond simple rule-following, actively observing their environment, making decisions, and taking actions to achieve specific goals . Key defining principles include:
· Autonomy: AI agents operate independently, choosing the best actions it needs to perform to achieve those goals rather than requiring constant human prompts or intervention.
· Rationality: They are rational agents, meaning they make rational decisions based on their perceptions and data to produce optimal performance and results .
· Learning and Adaptability: Advanced agents can continuously optimize their responses because they learn with every interaction . They adapt over time and integrate new feedback to create more updated guidelines .
· Multimodal Capability: Powered by generative AI and foundation models, AI agents can process diverse information types like text, voice, video, audio, code, and more simultaneously .
2. How AI Agents Work: The Perception-Decision-Action Loop
AI agents operate through a continuous cycle of sensing, processing, deciding, and acting:
· Perception (Collecting Information): Agents gather information from their surroundings. This can involve parsing text commands, analyzing data streams, or receiving sensor data , such as cameras and radar to detect objects for a self-driving car . The perception module converts raw inputs into a format the agent can understand and process .
· Decision-making & Planning (Processing Information): After gathering data, agents analyze it to determine the best course of action. This involves using machine learning models like NLP, sentiment analysis, and classification algorithms to evaluate their inputs against their objectives . Advanced agents may employ search and planning algorithms to find action sequences that lead to their goals .
· Knowledge Management: Agents maintain internal knowledge bases that contain domain-specific information, learned patterns, and operational rules . They can dynamically access this information using techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to form accurate and contextual responses.
· Action Execution (Performing Tasks): Once a decision is made, agents execute actions through their output interfaces . This includes generating text responses, updating databases, triggering workflows, or sending commands to other systems .
· Learning and Adaptation (Improving Over Time): Many AI agents continuously refine their behavior. They analyze the outcomes of their actions, update their knowledge bases, and refine their decision-making processes based on success metrics and user feedback , often using reinforcement learning techniques .
3. Key Benefits of AI Agents
The deployment of AI agents offers significant advantages for businesses:
· Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By automating repetitive tasks such as claims processing, appointment scheduling, or customer inquiries , AI agents free human employees to focus on more strategic responsibilities . This leads to 4x faster turnaround and increased output .
· Improved Accuracy: AI agents can analyze patterns and make data-driven decisions, which results in more accurate decisions for tasks that require extensive data analysis or pattern detection .
· Real-time Decision Making: Their ability to process vast amounts of data quickly enables AI agents to make real-time decisions in dynamic environments like financial markets or customer service .
· Personalization: Agents can take specifications and create a personalized experience that accounts for individual factors or preferences, such as suggested products for online shopping based on your past purchases .
· Cost Savings: By automating tasks and improving efficiency, AI agents can significantly reduce operational costs .
· Scalability: AI agents can handle large volumes of tasks simultaneously, making them ideal for scaling operations .
· Enhanced Customer Experience: They provide responsive, natural language support that enhances the user experience , leading to seamless support and improving customer satisfaction .
4. Classifications and Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be categorized by their decision logic, functional roles, or interaction patterns.
4.1. By Decision Logic (or Type of Agent)
These categories highlight how an agent processes information and selects actions:
·
Simple Reflex Agents:
· Definition: Act based on predefined rules and respond to specific conditions without considering past actions or future outcomes. They execute a preset action when they encounter a trigger .
· How they work: Use if this then that rule or condition-action rules . They have no memory or learning capabilities.
· Examples: Fraud flagging in banking, automatic email acknowledgments for claim submissions , thermostat turning on heat below a certain temperature , motion sensor lights .
· Limitations: Limited in adaptability; cannot handle complex scenarios and may get stuck in infinite loops in partially observable environments .
· Model-Based Reflex Agents:
· Definition: Create an internal model of their environment, allowing them to consider past states when making decisions . They operate in partially observable environments .
· How they work: Maintain an internal representation, or model, of the world , tracking how the environment evolves independent of the agent and how the agent’s actions affect the environment .
· Examples: Inventory tracking in supply chain, loan processing by verifying applicant documents , smart home security systems , self-driving cars .
· Advantages: Better suited for dynamic environments than simple reflex agents , can adapt to minor changes in the environment .
· Goal-Based Agents:
· Definition: Make decisions aimed at achieving a specific outcome . They evaluate different actions to find the ones that best move them closer to their defined goals .
· How they work: Use search and planning algorithms to find action sequences that lead to their goals . They are flexible and can replan if the environment change .
· Examples: Logistics routing agents , industrial robots for assembly , GPS navigation systems , project management systems .
· Utility-Based Agents:
· Definition: Work towards goals and maximize a 'utility' or preference scale . They handle tasks with multiple possible solutions, evaluating which one yields the best overall outcome .
· How they work: Use a utility function to assign a score to different options and then it picks the best one . They aim to maximize expected utility, ensuring they make the most favorable decision under uncertain conditions .
· Examples: Financial portfolio management agents , resource allocation systems , stock trading bots , smart building management , self-driving cars evaluating safest, fastest, and most fuel-efficient routes .
· Challenges: Complexity of utility calculations and potential for misaligned utility .
·
Learning Agents:
· Definition: Adapt and improve their behavior over time based on experience and feedback . They are also considered predictive agents .
· How they work: Modify their behavior based on feedback and experience , often using machine learning techniques and a problem generator to explore new actions .
· Examples: E-commerce recommendation engines , customer service chatbots that improve response accuracy , Netflix content recommendations .
· Multi-Agent Systems (MAS):
· Definition: Consist of several AI Agents working collaboratively or competitively within a shared environment . Each agent specializes in a task, allowing them to handle more complex, interdependent workflows .
· How they work: Agents communicate and coordinate to achieve shared or individual goals, employing communication protocols and coordination mechanisms .
· Examples: Smart city traffic management systems , internal AI Agents (Document AI, Decision AI, etc.) working seamlessly together , swarm robotics , Miovision Adaptive traffic signal optimization .
· Advantages: Scalable for complex, large-scale applications and offers redundancy and robustness .
· Challenges: Complexity in coordination and conflict resolution .
·
Hierarchical Agents:
· Definition: Operate across different levels, each responsible for distinct tasks or decisions within a structure . They combine multiple agent types into a hierarchy .
· How they work: Higher-level agents manage and direct the actions of lower-level agents , breaking down complex tasks into manageable subtasks .
· Examples: Quality control in manufacturing , autonomous drone operations , smart factories , Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robotics .
4.2. By Functional Roles within Businesses
These categories describe the business purpose of the AI agent:
· Customer Agents: Designed to engage with users, answer inquiries, and handle routine customer service tasks, usually 24/7 . Example: Volkswagen US virtual assistant in myVW app .
· Employee Agents: Assist in HR, administrative, and productivity tasks . Example: Onboarding agents for new employees, Uber's driver onboarding optimization .
· Creative Agents: Support content creation by generating text, images, or video content based on specific inputs . Example: PUMA generating customized product photos using Imagen , resume-writing AI agents .
· Data Agents: Handle large-scale data processing tasks, from data cleaning to analytics , acting as information retrieval agents to extract insights from massive datasets . Example: Financial institution data analysis agents, Database AI for sales representatives .
· Code Agents: Assist software developers in creating and maintaining applications and systems by tasks like bug detection, code optimization, and snippet generation . Example: Replit, Vercel, Lovable, GitHub Copilot , Google Cloud Vertex AI Agent Builder .
· Security Agents: Monitor systems continuously, detect anomalies, and respond to threats in real-time . Example: Banking applications detecting fraudulent transactions, Microsoft Security Copilot .
4.3. Emerging and Hybrid Agent Types
As AI advances, new and combined agent types are emerging:
· Hybrid Agents: Integrate features from multiple agent types, enabling them to address tasks that require balancing competing objectives, long-term planning, and real-time adaptability . Examples include Goal-Utility Hybrids (optimizing goal achievement with efficiency, e.g., logistics minimizing fuel and time) and Learning-Utility Hybrids (adapting strategies over time for optimal results, e.g., stock trading).
· Multi-Modal Agents: Combine different input modalities like visual, auditory, and text-based data for more comprehensive decisions . Example: Autonomous vehicles integrating road visuals, GPS, and traffic data.
· Collaborative Hybrid Systems: Multiple agents with hybrid capabilities working together, often in decentralized environments . Example: Swarm robotics for disaster recovery.
5. Challenges of Implementing AI Agents
Despite the numerous benefits, deploying AI agents comes with considerations:
· Computational Costs and Resources: Running AI agents can require significant computing power, storage, and memory resources, as well as trained staff , leading to sizable upfront costs and extensive planning .
·
Human Training and Oversight: While autonomous, agents do require some human training and general oversight to ensure the models are operating properly .
·
Integration Difficulties: Not all AI agent types can work together in hybrid or multi-agent systems , requiring careful testing for compatibility.
· Infinite Loops: Agents can enter an endless cycle of actions if not properly designed, affecting data quality and use up costly resources .
· Data Privacy Concerns: Advanced agents handle massive volumes of data, necessitating necessary measures to improve data security posture .
·
Ethical Challenges and Bias: Deep learning models may produce unfair, biased, or inaccurate results if trained on biased data. Ensuring fairness and transparency in their decision-making processes is essential .
· Technical Complexities: Implementing advanced agents requires specialized experience and knowledge of machine learning technologies .
· Tasks Requiring Deep Empathy/Emotional Intelligence: AI agents can struggle with nuanced human emotions and lack the moral compass and judgment needed for ethically complex situations .
6. Choosing the Right AI Agent
Selecting the appropriate AI agent involves a systematic approach:
·
Assess Needs and Goals: Clearly define your project’s needs and goals . Identify specific tasks, define desired outcomes (e.g., efficiency, cost reduction, customer experience), and understand the operating environment (fully vs. partially observable, static vs. dynamic).
·
Evaluate Options: Consider factors like:
· Complexity: Simple reflex agents are easier but less adaptable; utility-based agents are complex but offer high optimization.
· Cost: Development, deployment, and maintenance costs vary significantly by agent type.
· Scalability: Can the agent handle increased workload or adapt to new tasks?
· Integration: How well will it integrate with existing systems?
· Implementation Considerations:Integration Planning: Ensure seamless data flow with existing systems.
· Performance Monitoring: Establish KPIs and alerts to track effectiveness.
· Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops to refine performance.
· Ethical Considerations: Address data privacy, bias, and transparency.
Businesses often leverage a range of AI Agents to streamline workflows, improve decision-making, and enhance customer satisfaction , with the understanding that automating business processes will typically require multiple AI agents working in sequence .
7. Industry Adoption and Future Outlook
AI agents are already transforming various sectors:
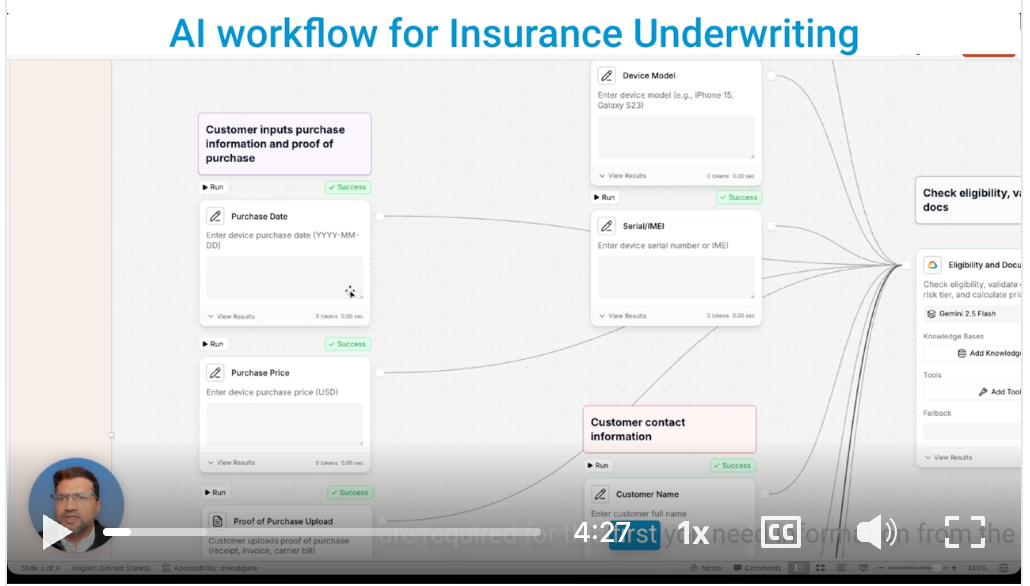
· Finance and Insurance: Automating end-to-end finance workflows securely for 4x faster turnaround , including credit rating, loan underwriting, life insurance, and P&C insurance automation.
· Healthcare: Streamlining workflows by scheduling appointments and providing initial diagnoses , assisting in personalized medicine and drug discovery .
· Retail and E-commerce: Enhancing shopping experiences with personalized product recommendations and real-time inventory management .
· Manufacturing: Automating quality control, optimizing supply chains, and improving production quality.
· Customer Service: Providing interactive support through virtual agents for billing inquiries or troubleshooting .
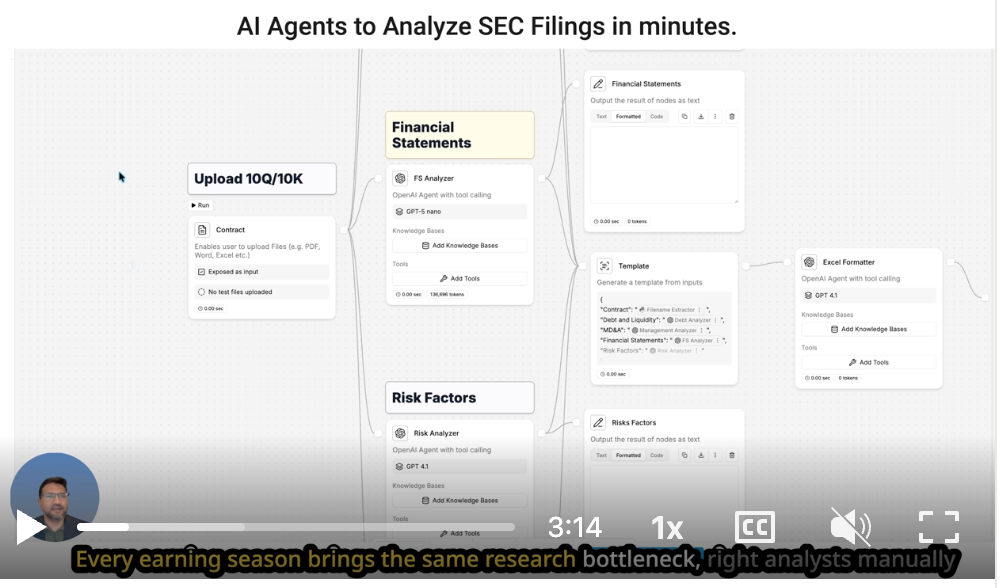
· Software Development: Speeding up the development lifecycle with code generation and optimization .
As AI technology continues to evolve, AI Agents are becoming more capable of working alongside humans in ways that were once limited to science fiction . The focus is on leveraging these agents for complex, multi-step troubleshooting and maximizing their potential through platforms that enable easy creation, management, governance, and integration into existing workflows.
References:
1. 13 Types of AI Agents (with Examples) (from AgentFlow): https://www.agentflow.ai/post/13-types-of-ai-agents-with-examples
2. 7 Types of AI Agents to Automate Your Workflows in 2025 (from DigitalOcean): https://www.digitalocean.com/blog/types-of-ai-agents
3. Agents in AI (from GeeksforGeeks): https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/agents-in-ai/
4. Exploring Different Types of AI Agents and Their Uses (from New Horizons):
https://www.newhorizons.com/blog/exploring-different-types-of-ai-agents-and-their-uses
5. L-7 | Types of AI Agents | Explained with examples (uploaded on the YouTube channel Code With Aarohi): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4zvvPar7Ybs
6. Exploring AI Agents: Types, Capabilities, and Real-World Applications (from Automation Anywhere, originally listed as Types of AI Agents: Choosing the Right One):
https://www.automationanywhere.com/blog/automation-ai/types-of-ai-agents
7. What are AI Agents? (from AWS): https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/
8. What are AI agents? Definition, examples, and types (from Google Cloud):
https://cloud.google.com/learn/what-are-ai-agents